In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, staying abreast of emerging technology trends is imperative and demands significant effort. Adopting and integrating new tools and technologies is a complex task fraught with challenges, such as conflicting deadlines, constrained resources, and productivity hurdles. These challenges underscore the necessity of effective time management strategies, such as the Four Quadrants of Time Management.
Effective time management is crucial in the business realm, especially during digital transformations involving SaaS solutions like ERP systems and other technological infrastructures. For a smooth transition, managers and teams should focus on tasks that significantly influence the success of these initiatives, steering clear of non-essential activities. Prioritizing tasks is essential for ensuring efficient and successful technology adoption.
Key Takeaways
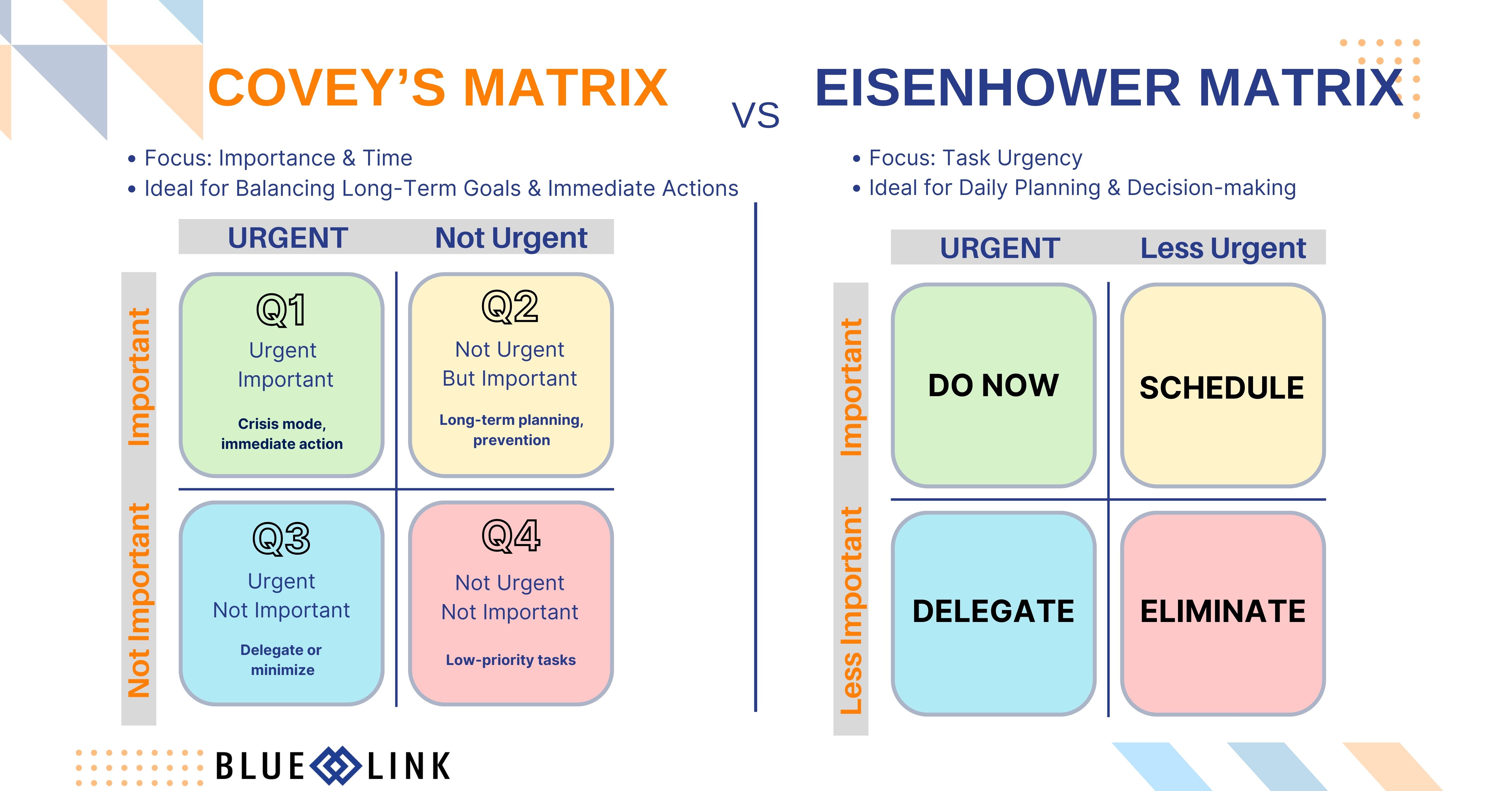
- The Four Quadrants of Time Management Framework (Covey's Matrix) is useful for aligning long-term goals with daily activities. You can measure tasks against two attributes, namely importance and urgency, and categorize them into four groups.
- The urgency of a task measures its time sensitivity and its immediate impact, especially on other tasks. The importance on the other hand measures the long-term impact and value of the task.
- Covey's matrix is a useful method to successfully address complicated projects such as SaaS implementation project planning and execution.
What Is the Four Quadrants of Time Management Framework?
The Four Quadrants of Time Management, also known as the Covey Time Management Matrix, was introduced by Stephen Covey in his best-selling book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.” Covey, an American businessman, speaker, and author, created this framework to help individuals and businesses prioritize tasks and optimize their time effectively. The matrix categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance, guiding users toward better decision-making and increased productivity. Its goal is to enhance personal and professional relationships, foster growth, and achieve meaningful accomplishments.
The concept is notably similar to the Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Eisenhower Decision Matrix, which was inspired by a quote attributed to former U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower. Eisenhower, a five-star general during World War II and the 34th President of the United States, frequently made critical decisions under immense pressure. He developed the matrix to prioritize and manage high-stakes issues throughout his military and political careers.
The primary distinction between the Covey Matrix and the Eisenhower Matrix lies in their focus. While the Eisenhower Matrix categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance, the Covey Matrix emphasizes the time allocated to tasks within each quadrant. Despite their similarities, the Covey Matrix offers a unique approach by concentrating on time management rather than the urgency and importance of tasks.
The Core Components of the Covey Time Management Matrix
The Covey Time Management Matrix is structured around two key attributes: urgency and importance. These attributes are represented on two perpendicular axes, like Cartesian coordinates. The horizontal axis (X-axis) represents urgency, indicating how immediate a task is, while the vertical axis (Y-axis) represents importance, measuring the impact of a task on overall performance, whether for an individual, team, or business. The intersection of these axes creates four distinct quadrants, each representing a different combination of urgency and importance.
Urgency vs Importance: What Are They, Exactly?
Although they may seem alike, important and urgent tasks are fundamentally different. Distinguishing between the two can be confusing, especially when managing multiple responsibilities. However, understanding this difference is crucial for effective time management and prioritization, especially if you want to use the 4 Quadrants of Time Management framework. In the following sections, we'll explore the concepts of urgency and importance, helping you have a better understanding of the time management matrix.
Urgent Tasks Explained
Urgent tasks demand immediate action, requiring attention either now or as soon as possible. Failing to complete them by their deadlines can lead to significant repercussions and increased stress due to their time-sensitive nature.
Examples of urgent tasks include:
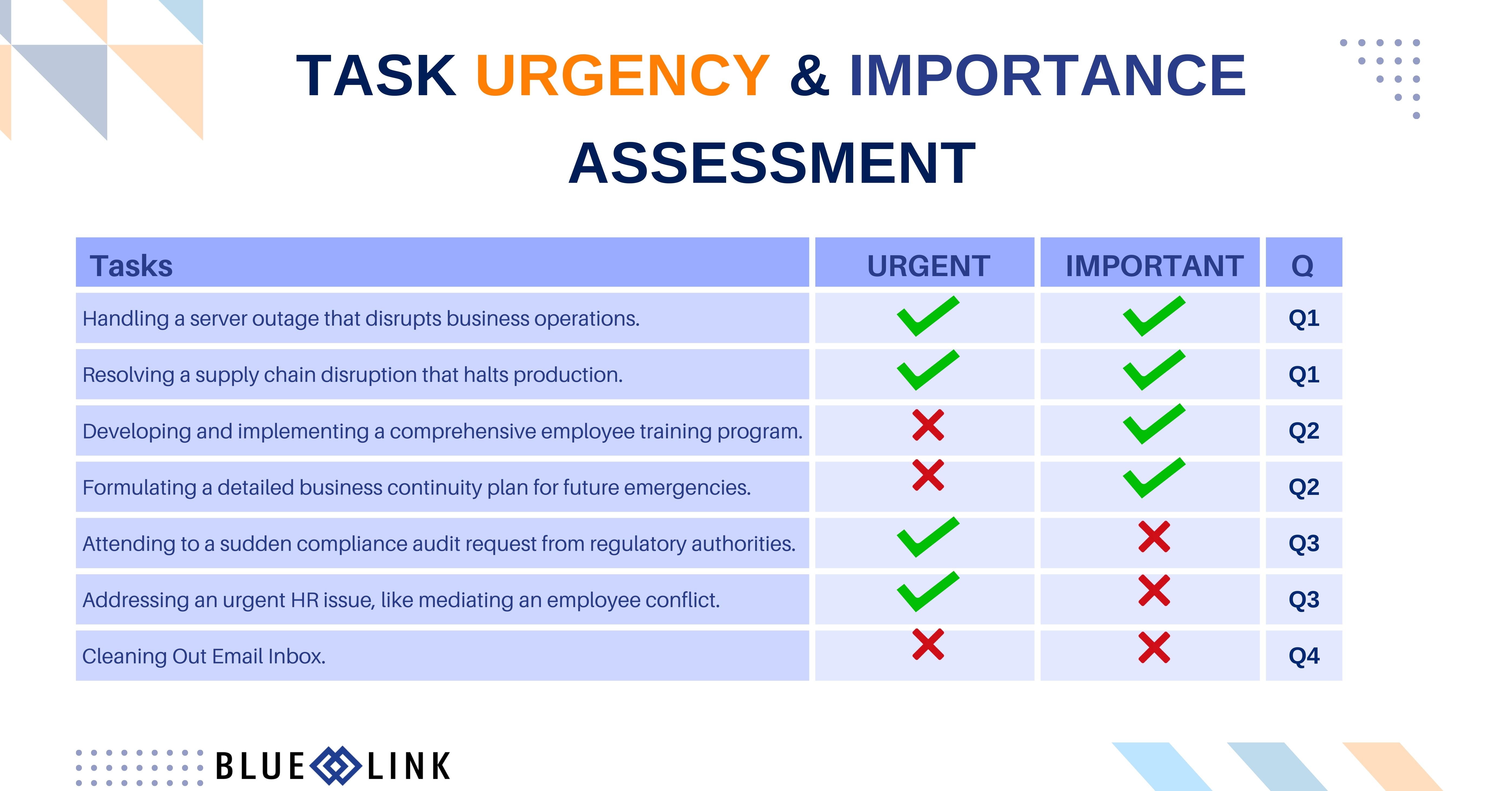
- Handling a server outage that disrupts business operations.
- Finalizing contract negotiations before an impending deadline.
- Attending to a sudden compliance audit request from regulatory authorities.
- Resolving a supply chain disruption that halts production.
- Addressing an urgent HR issue, like mediating an employee conflict that affects team dynamics.
What Are Important Tasks?
Important tasks contribute to long-term goals and serve as the foundation for other projects. Without these tasks, managing your final tasks or achieving sustained progress would be challenging. Even though they may not be urgent, important tasks have a lasting impact both professionally and personally.
Examples of important tasks include:
- Developing and implementing a comprehensive employee training program.
- Formulating a detailed business continuity plan for future emergencies.
- Establishing a customer feedback system to gather insights for continuous improvement.
- Designing a robust data security strategy to protect sensitive information.
- Engaging in strategic planning meetings to align departmental goals with overall business objectives.
- Creating a content calendar to ensure consistent and high-quality marketing efforts year-round.
How Does the 4 Quadrants of Time Management Framework Function?
The difficulty and urgency of tasks are mapped as the X and Y axis of the quadrant, creating 4 different areas. To implement the Four Quadrants of Time Management framework, you need to start by making a list of all tasks you must carry out within a timeframe. Each task needs to be assessed against each of the two attributes:
- Is the task Urgent or Not Urgent?
- Is the task Important or Not Important?
After assigning attributes to all the tasks, you can put them in 4 groups or quadrants:
1. Q1: Urgent and Important: Do First!
Tasks in the “Urgent and Important” quadrant (Q1) have distinct characteristics: they demand immediate attention due to pressing deadlines, are vital for achieving specific goals or meeting critical milestones, and help mitigate risks when addressed promptly. To manage Q1 tasks effectively, it is crucial to allocate adequate time and effort to them, avoid procrastination to prevent stress and negative outcomes, and maintain focus by minimizing distractions and concentrating on urgent issues.
2. Q2: Not Urgent but Important: Schedule!
Tasks in the “Not Urgent but Important” quadrant (Q2) are essential for achieving long-term goals and enhancing overall well-being, even though they don't demand immediate attention. These tasks include proactive planning, self-improvement, and preventive measures. Allocating time for Q2 activities with discipline and focus is crucial to prevent them from becoming urgent later. Treat these tasks as non-negotiable commitments to your future success and avoid procrastination.
3. Q3: Urgent but Not Important: Delegate!
The “Urgent but Not Important” quadrant (Q3) is characterized by interruptions that demand immediate attention but lack true significance in the grand scheme. These tasks often arise unexpectedly and can disrupt your focus on more important matters (distractions). To handle Q3 tasks effectively, consider delegating them to others or minimizing their impact. Evaluate whether they truly require your personal attention, set boundaries to limit the time spent on Q3 activities to avoid neglecting more important tasks, and avoid over-commitment by saying “no” when appropriate to prevent Q3 overload.
4. Q4: Not Urgent and Not Important: Limit!
Tasks falling into the “Not Urgent and Not Important” quadrant (Q4) are characterized by their low priority, meaning they don’t significantly impact your goals or well-being. These tasks often include trivial activities or distractions (time-wasters). To handle Q4 tasks effectively, consider reducing the time spent on them or eliminating them altogether. Discard or delegate these tasks whenever possible to free up mental space for what truly matters. Focus on higher priorities by investing your time in more meaningful activities that align with your goals, ensuring that your efforts contribute to your success and well-being.
Key Benefits of Using the Four Quadrants of Time Management
The Four Quadrants of Time Management offers numerous advantages for individuals and teams aiming to enhance productivity and balance their responsibilities. Here are the key benefits:
1. Boosted Productivity
By focusing on what truly matters, you can vastly improve productivity. Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance allows for informed decisions about time and effort allocation, leading to more efficient goal progression. When teams use this matrix to align their efforts, collaboration is more effective, further enhancing overall team efficiency.
2. Reduced Stress
The matrix simplifies complex tasks into manageable segments, alleviating the stress of trying to do everything at once. By refining your list of priorities and deciding which tasks to delegate, delay, or eliminate, you can significantly reduce feelings of overwhelm and stress.
3. Enhanced Work-Life Balance
Prioritizing tasks ensures that professional responsibilities are effectively managed, freeing up more time for personal pursuits and relaxation. Balancing urgent and important tasks helps maintain attention to personal life, fostering a healthier work-life balance.
4. Positive Habit Formation
Using the matrix promotes the development of positive habits by shifting focus from immediate demands to long-term, important goals. This transition helps break the cycle of urgency-driven prioritization and establishes sustainable, productive habits.
5. Increased Satisfaction
Proactive decision-making facilitated by the matrix enhances self-efficacy and overall satisfaction with both work-related and personal choices. This process leads to greater contentment and a more fulfilling life.
6. Long-Term Growth
Investing time in relationships, skill development, and long-term goals is crucial for personal and professional growth. The matrix ensures these important areas receive the attention they deserve, fostering sustained progress and development.
Implementing Covey's Time Management Matrix can revolutionize your approach to daily tasks, leading to a more organized, productive, and satisfying working style or team culture.
Four Quadrants of Time Management in Practice: SaaS Implementation
Real-life use cases of a tool are invaluable for gaining a deep understanding, particularly when transitioning from theoretical knowledge to practical application. To enhance your grasp of the framework, we will implement the Covey Time Management Matrix within the context of SaaS implementations.
Blue Link ERP Software serves as a prime example of a SaaS solution, specializing in wholesale, and distribution, especially in regulatory markets such as the pharmaceutical and food and beverage industries. Blue Link is dedicated to supporting its clients throughout the ERP implementation process, from data migration to user training.
While adopting new and innovative solutions can be costly, complex, and sometimes counter-intuitive, the success of a technology implementation project largely depends on effective change management strategies. Software solutions will not achieve their promised high ROI unless the implementation plan is closely aligned with business objectives and sufficient resources are allocated during the implementation phase. The Four Quadrants of Time Management framework aids in the successful implementation of SaaS solutions by helping teams prioritize tasks with higher importance.
The Critical Role of SaaS and Cloud Solutions in Modern Business Success
Software as a Service (SaaS) and cloud solutions, including ERP software, are pivotal to business success. They offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced mobility. By eliminating the need for end-user licenses and infrastructure, SaaS enables businesses to scale effortlessly according to their needs, avoiding hefty upfront costs with predictable monthly subscriptions. These solutions also support remote work, allowing employees to access applications and data from anywhere, which boosts productivity and collaboration.
Moreover, cloud solutions provide rapid deployment and updates, making companies more agile and accelerating product releases. SaaS providers invest significantly in robust security measures, ensuring data protection and compliance with industry standards like CSOS (Controlled Substance Ordering System) and SOM (Suspicious Order Monitoring), which can be more challenging with traditional software. This transformation allows businesses to focus on their core competencies.
Additionally, ERP software delivered via SaaS streamlines operations, enhances efficiency, and integrates various business functions. This enables businesses to concentrate on what truly matters: serving customers and achieving sustainable growth. SaaS and ERP statistics in 2024 show that ERP solutions were among the most renewed SaaS categories, highlighting their critical role in driving business growth.
The Importance of Time Management in SaaS Implementation
Effective time management is crucial during a digital transformation due to the project's complexities. Similarly, replacing a legacy system demands meticulous planning and precise time allocation to ensure seamless implementation and minimize disruptions.
Data security demands significant attention, involving the implementation of rigorous encryption, stringent access controls, and compliance with regulatory measures to protect sensitive information stored on third-party servers. This continuous process necessitates ongoing vigilance.
There are some SaaS solutions that are designed with functionality for specific industries while others offer a more standardized nature. Either way, your business may still have specific processes that have been developed in-house causing a slight limitation. Addressing these limitations requires careful vendor coordination and strategic planning to balance standardization with necessary customizations. Managing scalability during periods of growth or peak usage also demands meticulous planning to maintain consistent performance.
Resistance to change from employees and managers can impede the adoption of new tools and technologies. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication about the benefits of SaaS and transparency of concerns. Training and support are vital; end-users must be well-prepared to use new software efficiently, necessitating comprehensive education and ongoing support to minimize disruptions and boost user confidence.
Insufficient planning can lead to delays and project failures. Developing a detailed, realistic implementation plan is essential. Allocating ample time for both the planning and execution phases is crucial for balancing standardization with customization effectively. By identifying specific requirements early and involving vendors, organizations can overcome challenges and ensure a successful implementation aligned with their unique needs and goals. Covey’s Matrix can be a valuable tool for project planning and time management in software implementation.
SaaS Implementation Roadmap: Best Practices
Recognizing and addressing the SaaS implementation challenges proactively, organizations can better navigate the complexities of digital transformation and SaaS implementation, ultimately driving innovation and achieving long-term success. A structured approach, encompassing thorough planning, meticulous execution, and ongoing support, is essential to navigate these complexities. This roadmap outlines best practices for each phase of SaaS implementation, ensuring that organizations can achieve their goals and maximize the value derived from their SaaS investments.
The initial phase involves identifying business requirements by evaluating current processes to identify improvement areas, and ensuring the selected SaaS aligns with business goals and needs. Next, organizations should evaluate vendor options by researching and comparing features, pricing, scalability, and support, and engaging stakeholders for a comprehensive assessment. Setting implementation and utilization goals is crucial, with clear definitions of key objectives, metrics, adoption scope, timeline, and utilization levels. A detailed implementation plan should be developed, outlining timelines, milestones, and responsibilities, and communicated effectively to manage expectations.
Involving IT teams and end-users early is important to gather insights and address concerns, ensuring the solution meets practical needs. Conducting thorough User Acceptance Testing (UAT) before full deployment ensures functionality and usability. Providing adequate training, support, and a detailed rollout plan, alongside forming a dedicated software implementation team, are essential steps. Organizing vendor implementation assistance for data migration, training, and onboarding, and clarifying support level agreements (SLAs) ensures effective assistance. Completing data migration securely, building initial tech stack integrations to streamline operations, and focusing on feature adoption by prioritizing critical functions and gradually introducing advanced features are key to maximizing efficiency and achieving long-term success.
Use Case of the Four Quadrants of Time Management in SaaS Implementation
As discussed previously, implementing SaaS is a significant transformation for any business, necessitating meticulous planning and management. The success of software and infrastructure deployment hinges on the quality of the planning and execution. Adopting a comprehensive approach to the software implementation roadmap can substantially boost ROI and facilitate business scaling.
The Four Quadrants of Time Management framework is particularly well-suited for this endeavor. By categorizing and prioritizing tasks within SaaS implementation, teams can allocate time and resources more effectively. This approach not only saves considerable time and capital but also enhances team productivity through positive engagement, workload reduction, and support for long-term objectives.
While technology implementation must be tailored to the unique characteristics and context of each business, generally, Covey’s Matrix for SaaS implementation would be:
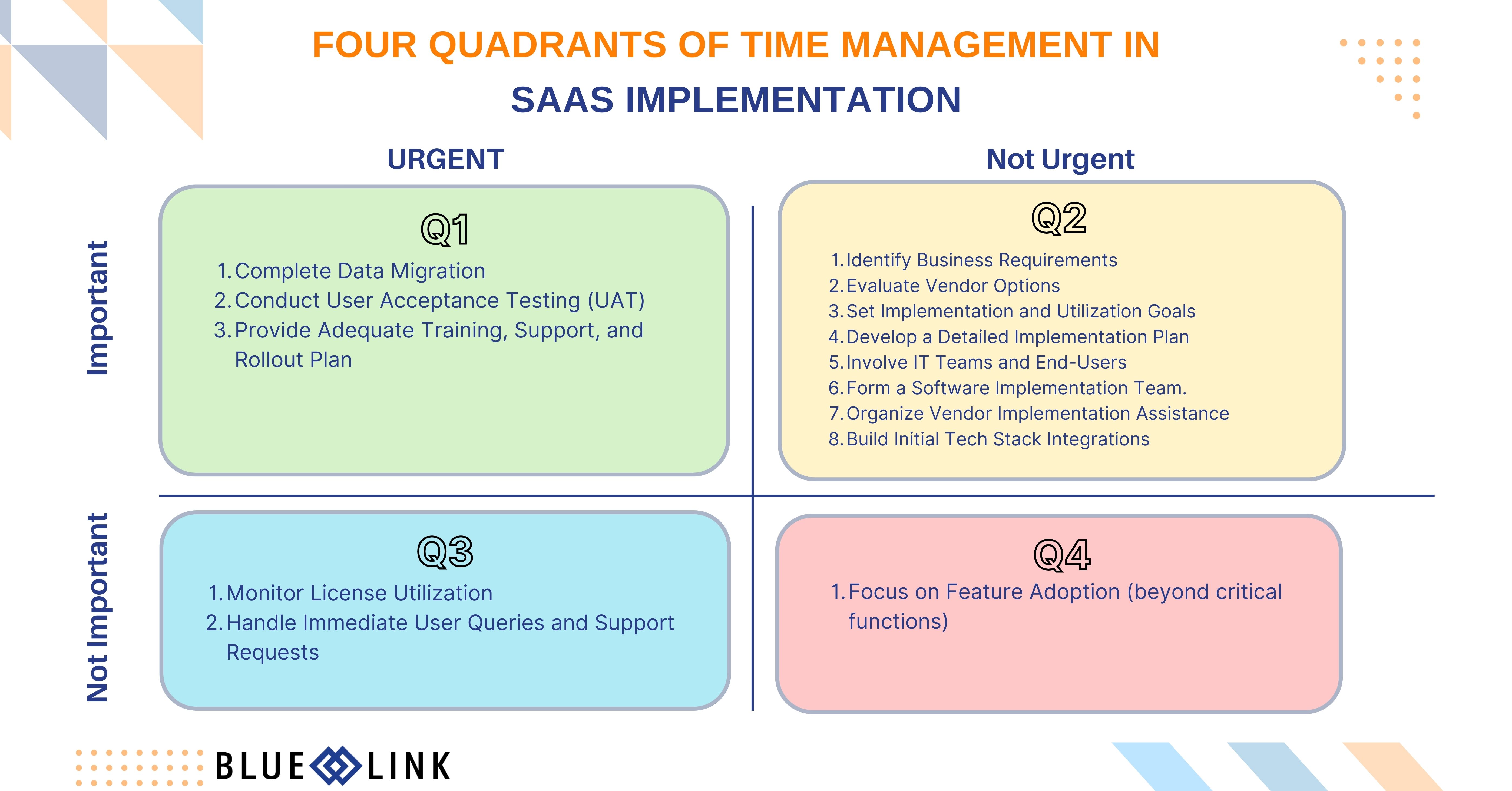
Quadrant 1: Urgent and Important Tasks in SaaS Implementation
Tasks that need immediate attention and are critical to the SaaS implementation success.
- Complete Data Migration: Ensuring data integrity and security during the transition to the new system is crucial to avoid business disruptions.
- Conduct User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Identifying and addressing any issues before full deployment is vital to prevent post-deployment problems.
- Provide Adequate Training, Support, and Rollout Plan: Immediate training is essential to ensure employees can use the new system effectively, reducing manual errors and improving productivity.
Quadrant 2: Not Urgent but Important Tasks in SaaS Implementation
Tasks that are essential for long-term success but do not require immediate action. These should be planned and scheduled.
- Identify Business Requirements: Evaluating current processes and defining needs to ensure the selected SaaS product aligns with business goals.
- Evaluate Vendor Options: Thorough research and comparison of different vendors to choose a solution adaptable for future growth.
- Set Implementation and Utilization Goals: Defining clear objectives and metrics to monitor progress and measure success.
- Develop a Detailed Implementation Plan: Outlining the entire process with timelines and responsibilities to manage expectations and ensure efficiency.
- Involve IT Teams and End-Users: Engaging stakeholders early to gather insights and address concerns, ensuring a smooth transition.
- Form a Software Implementation Team: Assembling a dedicated team to manage all aspects of the implementation effectively.
- Organize Vendor Implementation Assistance: Planning for vendor support in areas such as data migration and user onboarding.
- Build Initial Tech Stack Integrations: Integrating systems to streamline operations and reduce manual labor.
Quadrant 3: Urgent but Not Important in SaaS Implementation
Tasks that require immediate attention but do not significantly impact long-term goals. These can often be delegated.
- Monitor License Utilization: Ensuring that the software licenses are used efficiently and additional resources are provided as needed.
- Handle Immediate User Queries and Support Requests: Addressing user issues quickly to maintain smooth operations.
Quadrant 4: Not Urgent and Not Important in SaaS Implementation
Tasks that are neither urgent nor important and can be minimized or eliminated.
- Focus on Feature Adoption (beyond critical functions): Introducing advanced features gradually to avoid overwhelming users. This is less critical initially and can be done over time as users become more comfortable with the system.
By organizing the SaaS implementation tasks into these quadrants, you can prioritize effectively, ensuring that urgent and important tasks are addressed promptly while planning and scheduling those that are crucial for long-term success. This structured approach aligns with the Covey Matrix methodology, facilitating a smoother and more efficient SaaS implementation process.
FAQs
How Can Covey's Matrix Help with SaaS Implementation?
Covey's Matrix helps in identifying and prioritizing tasks related to SaaS implementation. By categorizing tasks into four quadrants, organizations can focus on critical activities such as data migration and user training (Quadrant I) while planning for long-term goals like developing a detailed implementation plan (Quadrant II).
What Are Some Common Challenges in SaaS Implementation, And How Does Time Management Help Address Them?
Common challenges include data migration issues, user resistance, inadequate training, and integration problems. Effective time management helps address these by prioritizing critical tasks, ensuring thorough planning and execution, and allocating resources efficiently to mitigate risks.
What Are the Common Pitfalls When Using The 4 Quadrants of Time Management, And How Can They Be Avoided?
Common pitfalls include over-focusing on urgent tasks (Quadrant I) at the expense of important long-term activities (Quadrant II). To avoid this, regularly review and adjust your priorities, and ensure time is dedicated to strategic planning and development.
How Do I Start Implementing the 4 Quadrants in My Workflow?
Begin by listing all your tasks and categorizing them into four quadrants. Focus first on urgent and important tasks (Quadrant I), then schedule time for important but not urgent tasks (Quadrant II). Delegate or minimize tasks in Quadrants III and IV.